



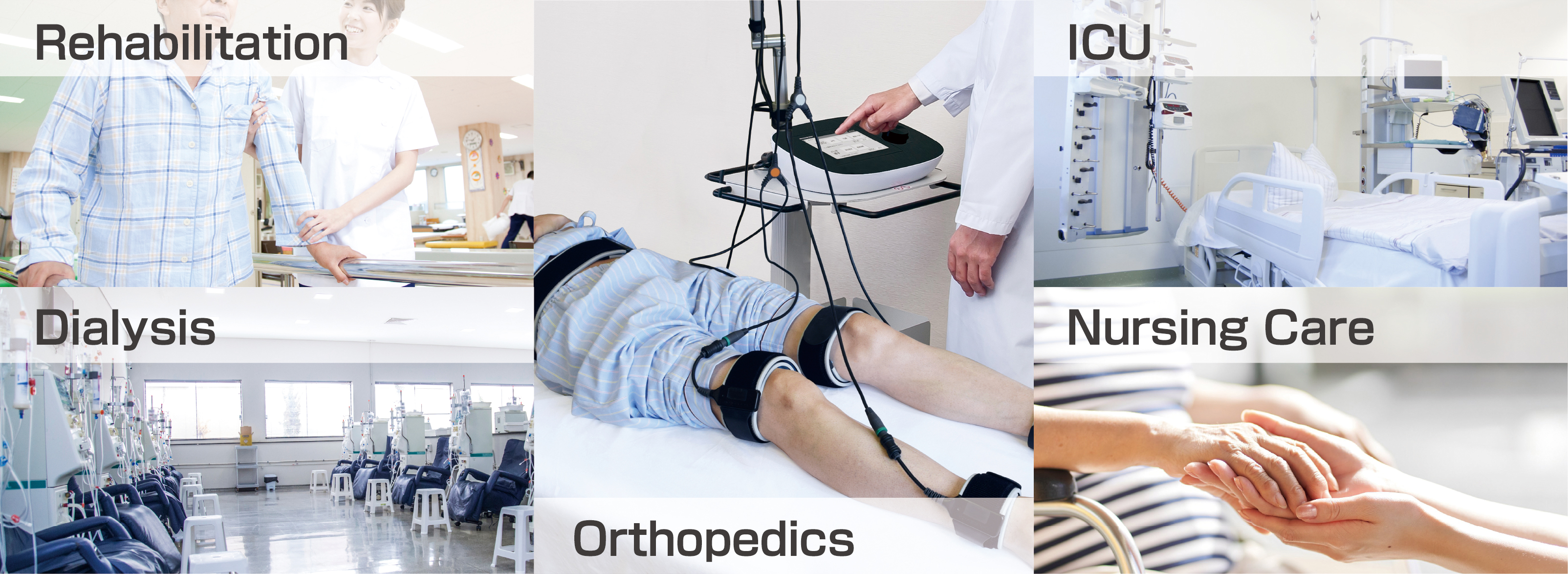
●Aging ●Unfamiliarity with exercise ●Pain
●Orthopedic disease ●Respiratory disease
●Cardiovascular disease ●ICU
(Examples of patients with possible muscle atrophy)
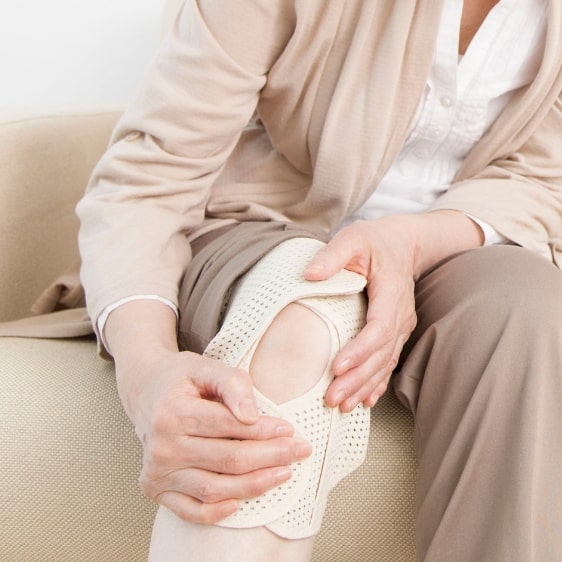
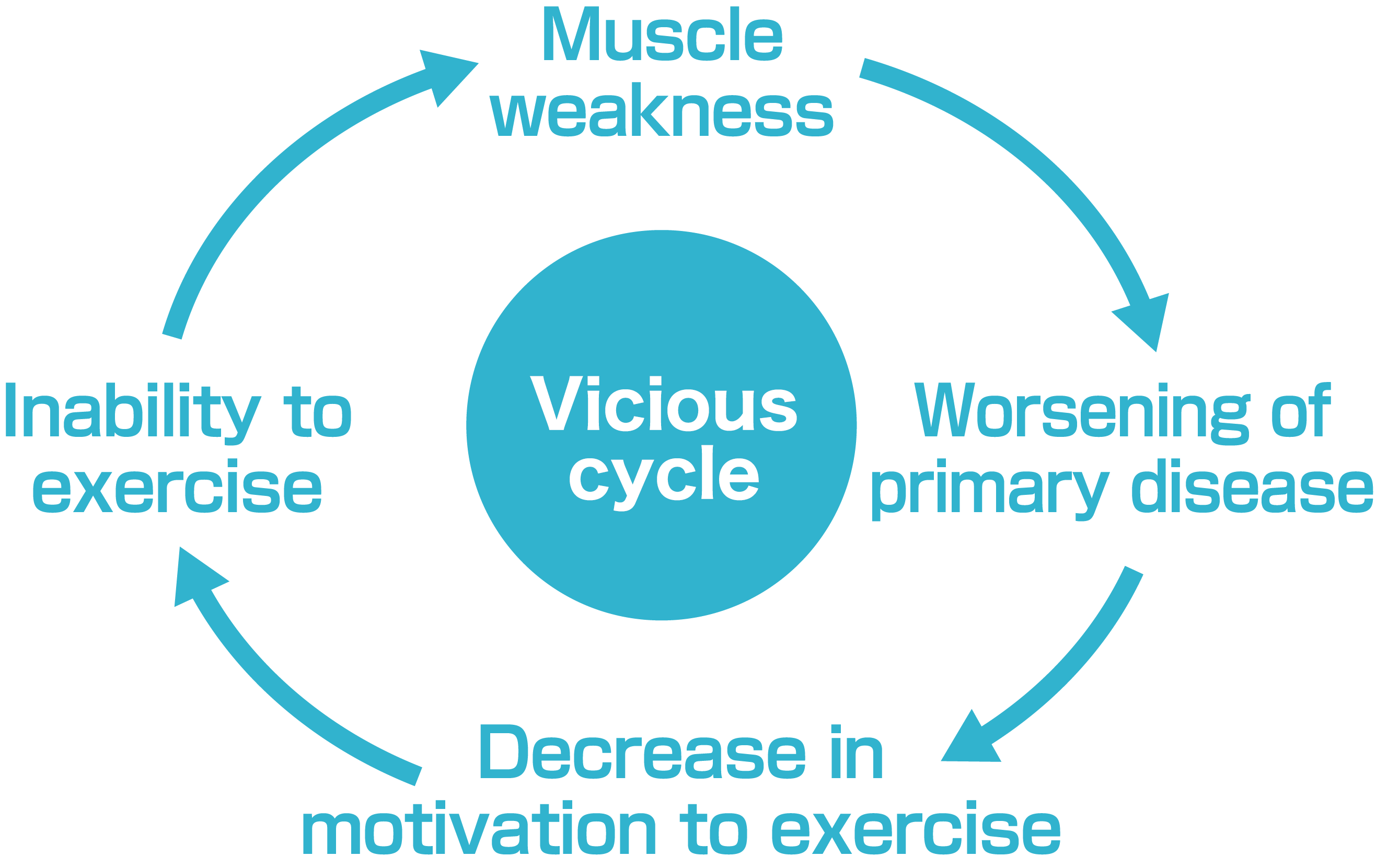



Lack of exercise due to aging, unfamiliarity with exercise, orthopedic disease, and diseases, such as respiratory /cardiovascular disorders, may cause muscle atrophy from disuse. Exercise-deficient people cannot exercise, which can lead to decreasing muscle strength, worsening of the primary disease to cause pain, and distress in exercise, as well as a decrease in the motivation to exercise. This further reduces the exercise quantity to repeat the vicious cycle.
"Cannot exercise" and "Do not exercise" individuals are at higher risk of bedridden or requiring care, so it is necessary to exercise.

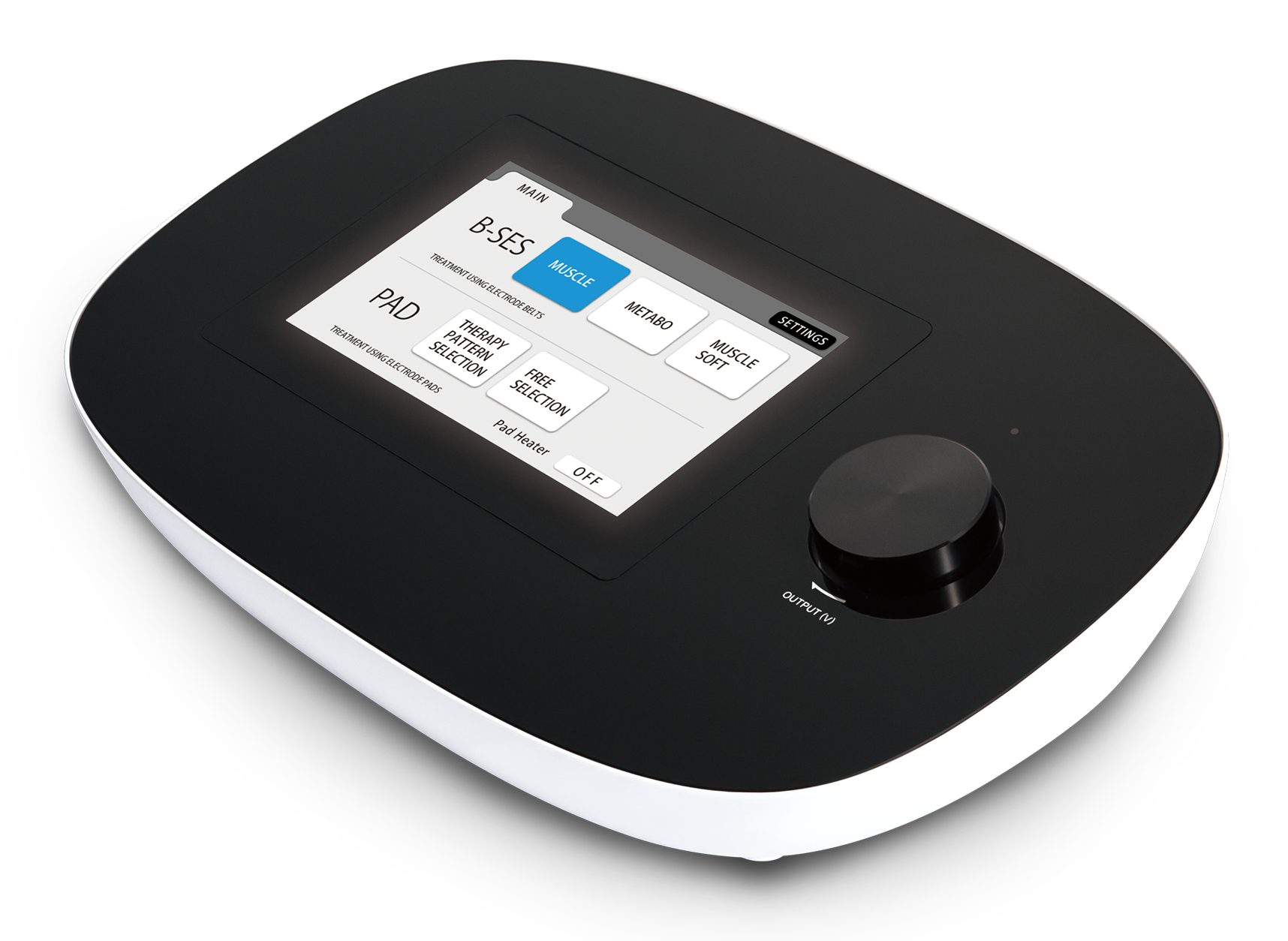
aerobic exercise depending on the intended purpose, and provides a substitute for exercise.

Perform strong muscle contractions at 20Hz for substitution of strength training.
Perform repeated single contractions at 4Hz for substitution of Aerobic exercise.

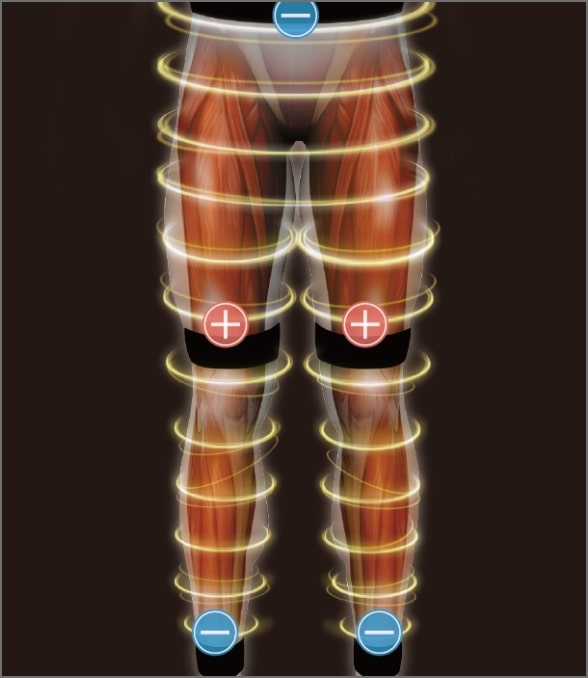
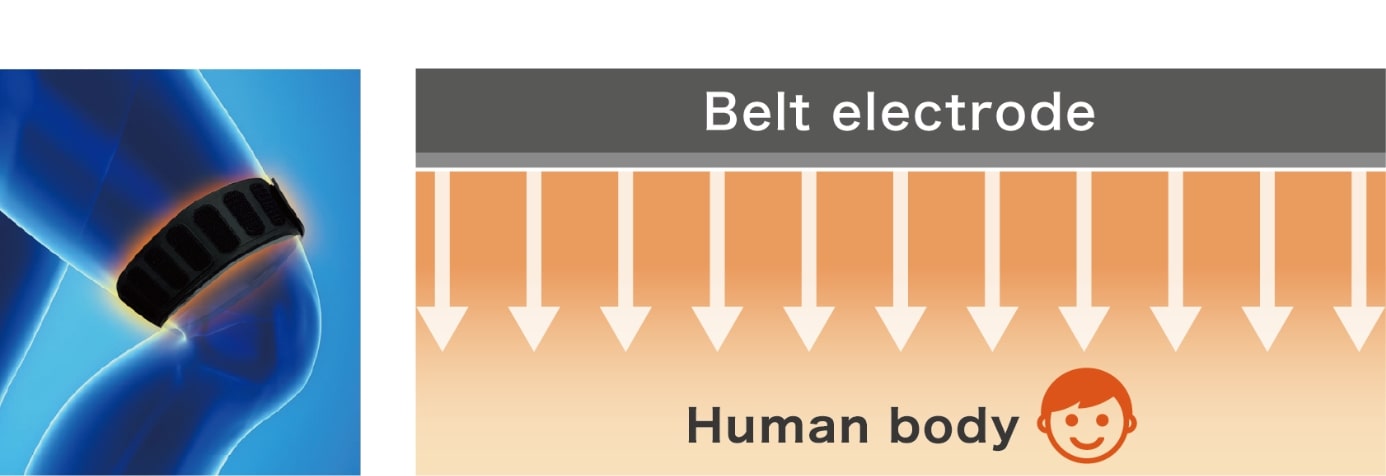
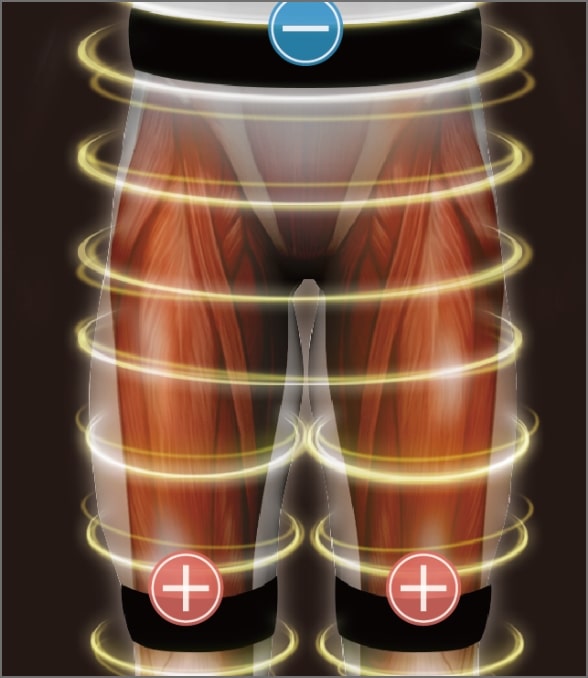
The belt electrodes deliver electricity cylindrically, allowing the stimulation of all muscles in the lower extremities.
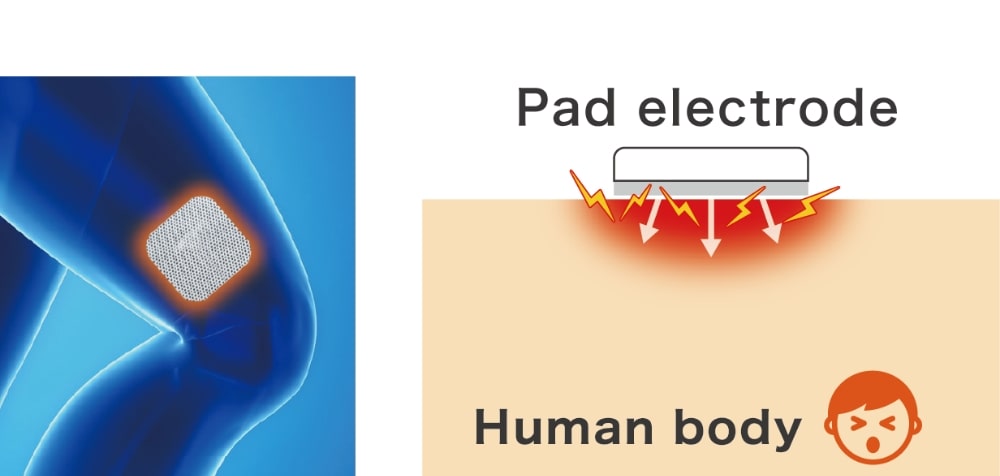
Since the electrode area is large and the skin's contact area is increased, the potential density is dispersed, making the electrode less painful and allowing high-intensity muscle contractions.

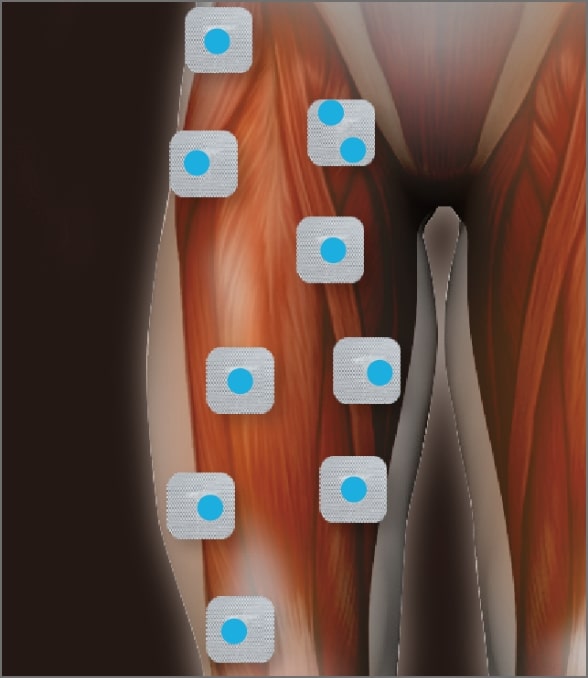
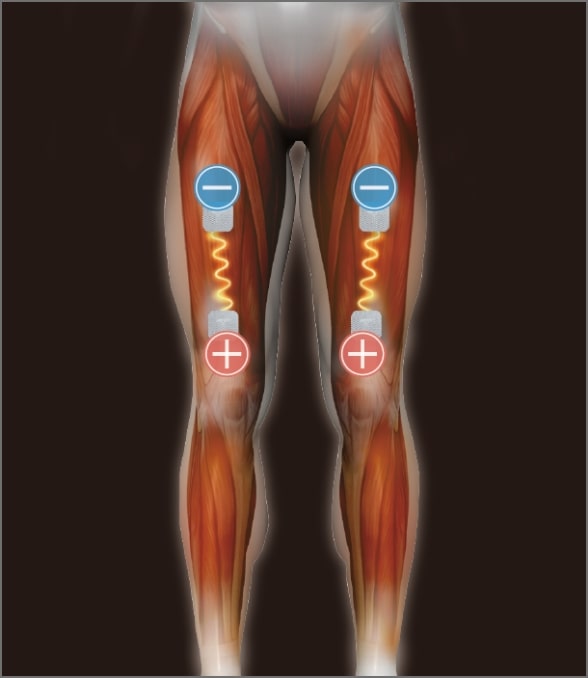
Motor points: Points with dense neuromuscular junctions to which current is applied to move the muscle
Since the electrode is large, anyone can perform the same treatment regardless of the motor point, and there is high treatment reproducibility.
| Pad | Belt | |
|---|---|---|
| Searching motor point | × | ○ |
| Number of electrodes | ×(many) | ○(few) |
| Treatment reproducibility | × | ○ |
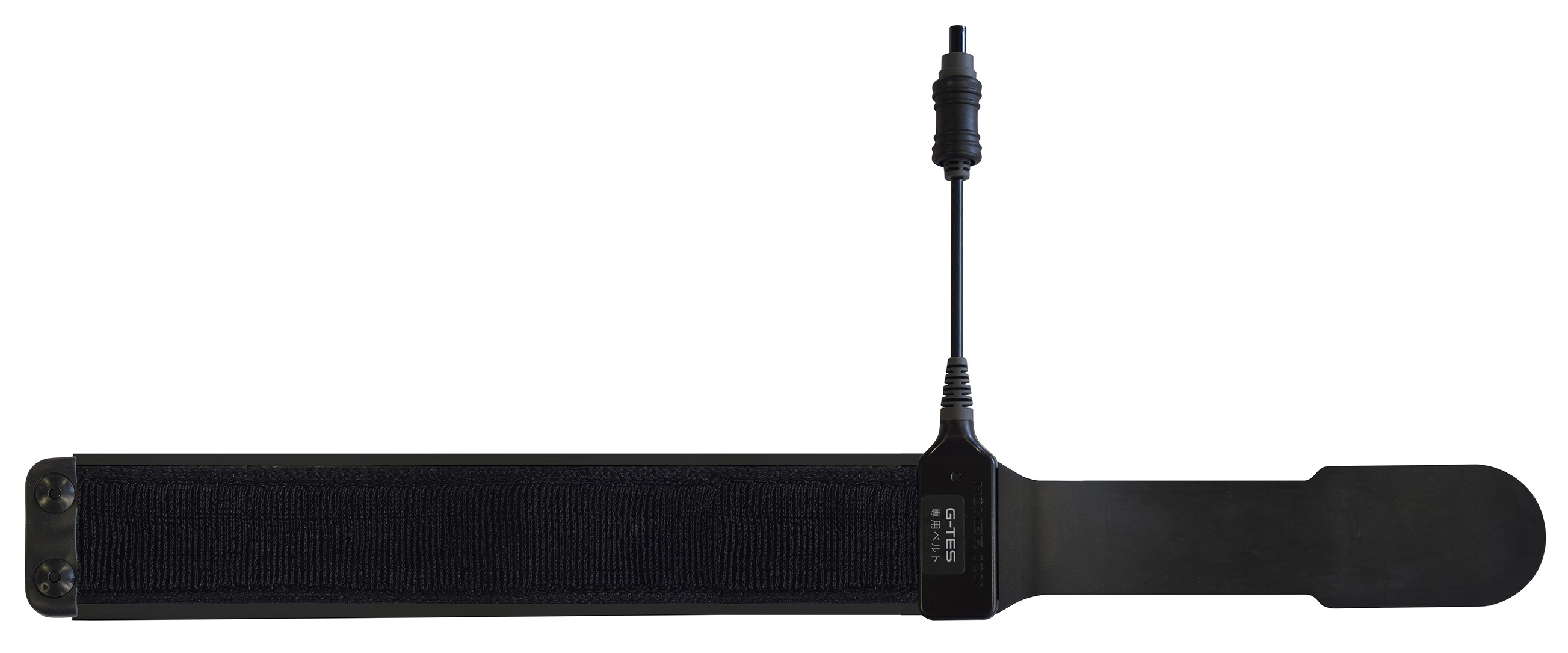

Belt electrode - Small

Belt electrode sheet - Small
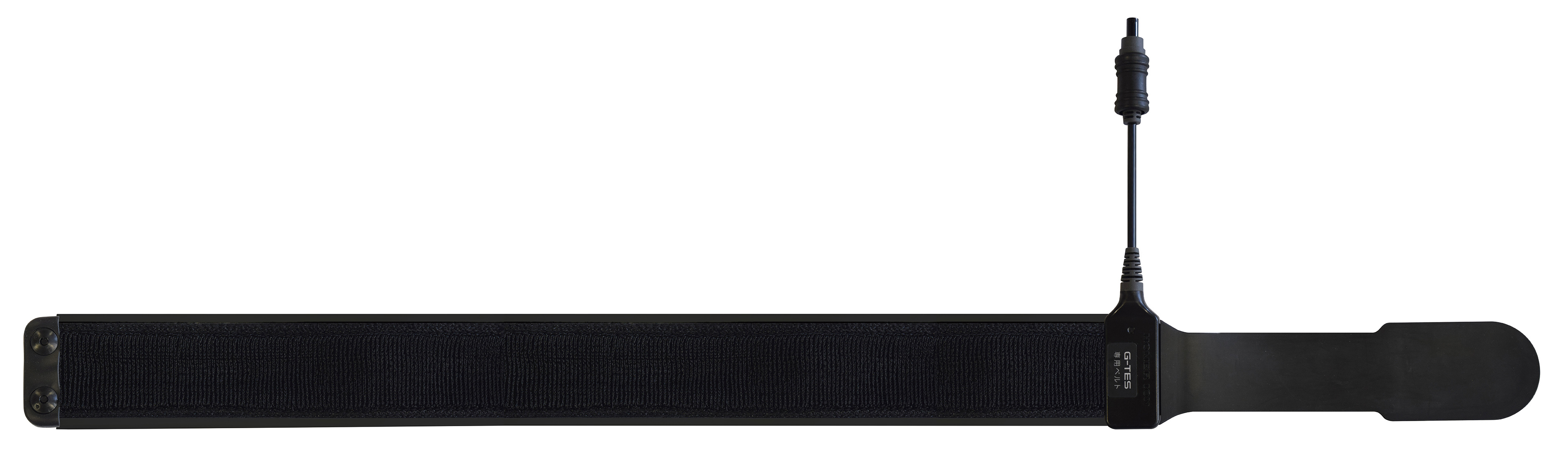

Belt electrode - Medium

Belt electrode sheet - Medium
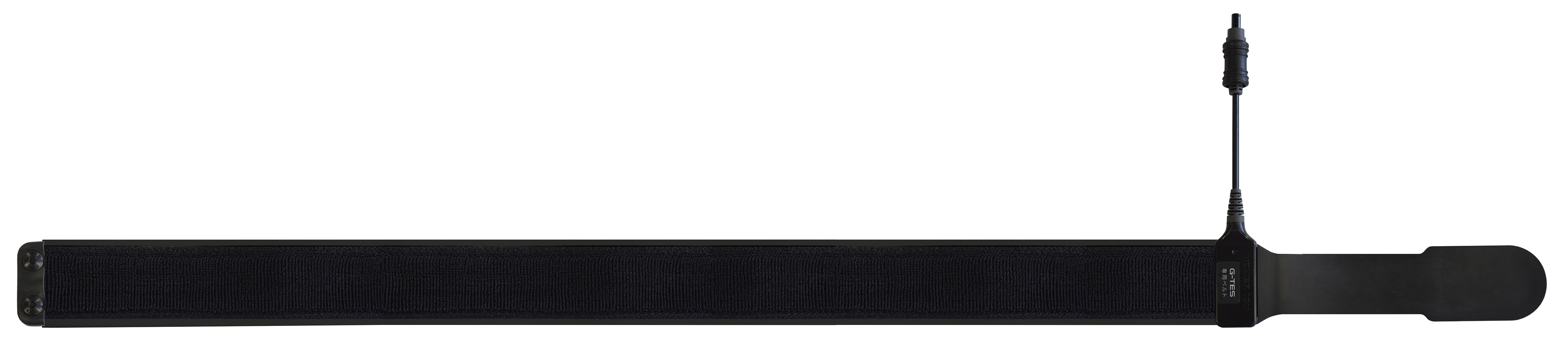

Belt electrode - Large

Belt electrode sheet - Large
Do not use on these patients.
Contact Us

